Overview

Heel pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. Heel pain is a problem which affects people of all ages and vocations, whether they are active or not and it comes in many different forms. Heel pain can also occur in children usually between the ages of 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities and during the growing phase.
Causes
Age plays a large role in the development of heel pain, particularly among those over 40. Being active is also a common factor of heel pain. Over time, the elasticity of the tissue in our feet decreases with age, causing us to become prone to damage and also slowing the body's ability to heal damage. Adolescents are also not immune to heel pain. Those who are active in sports are particularly prone to excessively stretching or straining the plantar fascia or Achilles tendon, causing severe heel pain. In most cases, heel pain develops in only one heel. There are many risk factors that lead to heel pain. Abnormal gait and excessive, repetitive stress are common factors in the development of pain and damage. Among the other risk factors involved with the development of heel pain are repetitive exercise or activities, such as long distance running or jumping from activities such as basketball. Obesity. Walking barefoot on hard surfaces. Prolonged standing. Wearing poor fitting shoes, or shoes that do not provide enough support or cushioning. Not stretching properly or at all before and after exercise. Those who are on their feet for long periods of time.
Symptoms
Pain in the bottom of the heel is the most common symptom. The pain is often described as a knife-like, pinpoint pain that is worse in the morning and generally improves throughout the day. By the end of the day the pain may be replaced by a dull ache that improves with rest. The pain results from stretching the damaged tissues. For the same reason atheletes' pain occurs during beginning stages of exercise and is relieved over time as warm-up loosens the fascia. Plantar fasciitis onset is usually gradual, only flaring up during exercise. If pain is ignored, it can eventually interfere with walking and overall, plantar fasciitis accounts for about ten percent of all running injuries.
Diagnosis
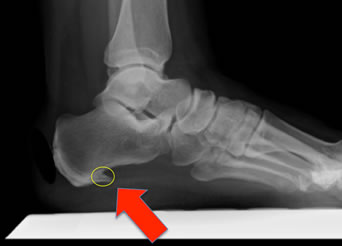
To arrive at a diagnosis, the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the surgeon rules out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis. In addition, diagnostic imaging studies such as x-rays or other imaging modalities may be used to distinguish the different types of heel pain. Sometimes heel spurs are found in patients with plantar fasciitis, but these are rarely a source of pain. When they are present, the condition may be diagnosed as plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome.
Non Surgical Treatment
Once diagnosed, treatment for plantar fasciitis may include one or more of the following: advice on footwear, in particular use of arch-supportive footwear; avoid walking barefoot; stretching exercises, shoe modifications such as heel pads, taping and strapping, anti-inflammatories and orthotic devices to correct abnormal foot mechanics. Injection therapy with corticosteroids is only advisable if all the conservative treatment methods mentioned above have been exhausted due to undesired effects implicated with steroid infusion in the heels.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
Why do I have pain in my heel?
Prevention
Make sure you wear appropriate supportive shoes. Don't over-train in sports. Make sure you warm up, cool down and undertake an exercise regime that helps maintain flexibility. Manage your weight, obesity is a factor in causing plantar fasciitis. Avoid walking and running on hard surfaces if you are prone to pain. You should follow the recognized management protocol "RICED" rest, ice, compression, elevation and diagnosis. Rest, keep off the injured ankle as much as possible. Ice, applied for 20 minutes at a time every hour as long as swelling persists. Compression, support the ankle and foot with a firmly (not tightly) wrapped elastic bandage. Elevation, keep foot above heart level to minimize bruising and swelling. Diagnosis. Consult a medical professional (such as a Podiatrist or doctor) especially if you are worried about the injury, or if the pain or swelling gets worse. If the pain or swelling has not gone down significantly within 48 hours, also seek treatment. An accurate diagnosis is essential for proper rehabilitation of moderate to severe injuries.

Heel pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. Heel pain is a problem which affects people of all ages and vocations, whether they are active or not and it comes in many different forms. Heel pain can also occur in children usually between the ages of 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities and during the growing phase.
Causes
Age plays a large role in the development of heel pain, particularly among those over 40. Being active is also a common factor of heel pain. Over time, the elasticity of the tissue in our feet decreases with age, causing us to become prone to damage and also slowing the body's ability to heal damage. Adolescents are also not immune to heel pain. Those who are active in sports are particularly prone to excessively stretching or straining the plantar fascia or Achilles tendon, causing severe heel pain. In most cases, heel pain develops in only one heel. There are many risk factors that lead to heel pain. Abnormal gait and excessive, repetitive stress are common factors in the development of pain and damage. Among the other risk factors involved with the development of heel pain are repetitive exercise or activities, such as long distance running or jumping from activities such as basketball. Obesity. Walking barefoot on hard surfaces. Prolonged standing. Wearing poor fitting shoes, or shoes that do not provide enough support or cushioning. Not stretching properly or at all before and after exercise. Those who are on their feet for long periods of time.
Symptoms
Pain in the bottom of the heel is the most common symptom. The pain is often described as a knife-like, pinpoint pain that is worse in the morning and generally improves throughout the day. By the end of the day the pain may be replaced by a dull ache that improves with rest. The pain results from stretching the damaged tissues. For the same reason atheletes' pain occurs during beginning stages of exercise and is relieved over time as warm-up loosens the fascia. Plantar fasciitis onset is usually gradual, only flaring up during exercise. If pain is ignored, it can eventually interfere with walking and overall, plantar fasciitis accounts for about ten percent of all running injuries.
Diagnosis
To arrive at a diagnosis, the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the surgeon rules out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis. In addition, diagnostic imaging studies such as x-rays or other imaging modalities may be used to distinguish the different types of heel pain. Sometimes heel spurs are found in patients with plantar fasciitis, but these are rarely a source of pain. When they are present, the condition may be diagnosed as plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome.
Non Surgical Treatment
Once diagnosed, treatment for plantar fasciitis may include one or more of the following: advice on footwear, in particular use of arch-supportive footwear; avoid walking barefoot; stretching exercises, shoe modifications such as heel pads, taping and strapping, anti-inflammatories and orthotic devices to correct abnormal foot mechanics. Injection therapy with corticosteroids is only advisable if all the conservative treatment methods mentioned above have been exhausted due to undesired effects implicated with steroid infusion in the heels.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
Why do I have pain in my heel?
Prevention

Make sure you wear appropriate supportive shoes. Don't over-train in sports. Make sure you warm up, cool down and undertake an exercise regime that helps maintain flexibility. Manage your weight, obesity is a factor in causing plantar fasciitis. Avoid walking and running on hard surfaces if you are prone to pain. You should follow the recognized management protocol "RICED" rest, ice, compression, elevation and diagnosis. Rest, keep off the injured ankle as much as possible. Ice, applied for 20 minutes at a time every hour as long as swelling persists. Compression, support the ankle and foot with a firmly (not tightly) wrapped elastic bandage. Elevation, keep foot above heart level to minimize bruising and swelling. Diagnosis. Consult a medical professional (such as a Podiatrist or doctor) especially if you are worried about the injury, or if the pain or swelling gets worse. If the pain or swelling has not gone down significantly within 48 hours, also seek treatment. An accurate diagnosis is essential for proper rehabilitation of moderate to severe injuries.




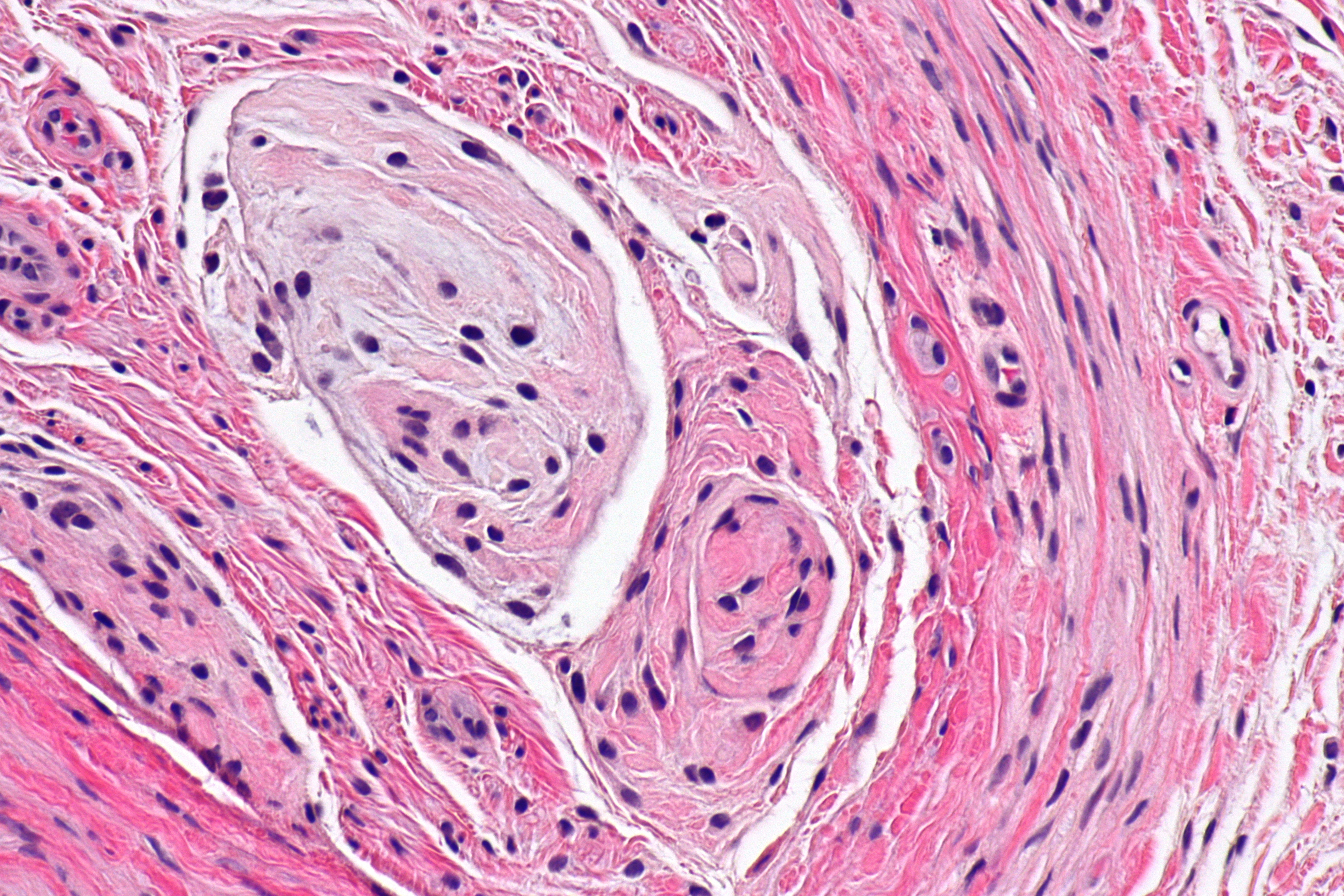 Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
Morton's neuroma is the common name given to the nerve irritation that is found in the ball of the foot that may or may not be accompanied by an inter-metatarsal bursae (a bursa-neuromal complex). It is often associated with inflammation or degeneration and often occurs with constant pressure or irritation of the nerve from the surrounding bony structures or local bursas (fluid filled sacs). Morton's Neuroma can cause symptoms such as a sharp pain, burning even a lack of feeling in the ball of the foot and associated toes.
 Overview
Overview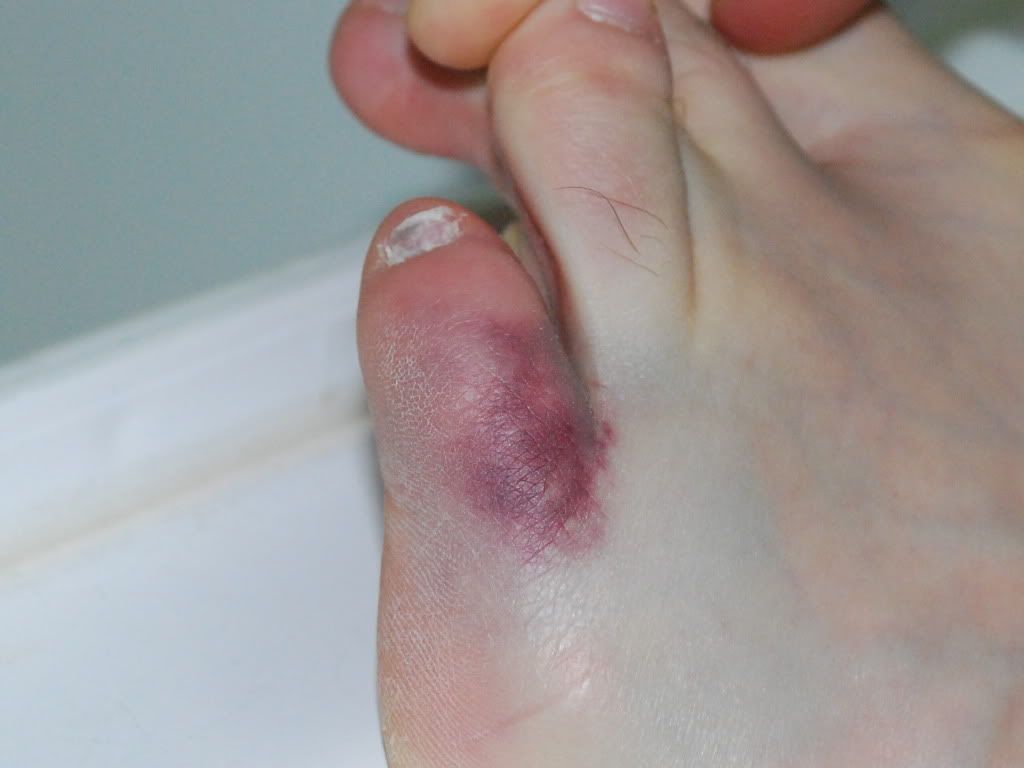
 A bunion (hallux abducto valgus) is a bony lump or enlargement that forms in the joint (metatarsal phalangeal joint) at the base of the big toe. The big toe points toward the other toes (lateral deviation) as the bunion progresses. The joint and surrounding tissue becomes inflamed and painful. Occasionally bunions can also form at the joint at the base of the smallest (fifth) toe. They are called a tailor's bunion or bunionette. Bunions can be accompanied by bursitis (inflammation of a small fluid-filled sac adjacent to the joint). With an advanced bunion the big toe may be so deformed that it has to lie over or under the second toe. In this situation it hurts to walk or wear any kind of shoe. About one in three people in most Western countries will get a bunion. They are about ten times more common in women than in men. Older people are more often affected than younger people, although bunions do occur in children with misaligned feet. Bunions should not be confused with gout or arthritis, which can also cause inflammation, deformity and pain around the toes and feet.
A bunion (hallux abducto valgus) is a bony lump or enlargement that forms in the joint (metatarsal phalangeal joint) at the base of the big toe. The big toe points toward the other toes (lateral deviation) as the bunion progresses. The joint and surrounding tissue becomes inflamed and painful. Occasionally bunions can also form at the joint at the base of the smallest (fifth) toe. They are called a tailor's bunion or bunionette. Bunions can be accompanied by bursitis (inflammation of a small fluid-filled sac adjacent to the joint). With an advanced bunion the big toe may be so deformed that it has to lie over or under the second toe. In this situation it hurts to walk or wear any kind of shoe. About one in three people in most Western countries will get a bunion. They are about ten times more common in women than in men. Older people are more often affected than younger people, although bunions do occur in children with misaligned feet. Bunions should not be confused with gout or arthritis, which can also cause inflammation, deformity and pain around the toes and feet.


 Complete Achilles tendon ruptures occur most commonly at the mid-substance, but also distally at the insertion site or proximally at the myotendinous junction. These can be traumatic and devastating injuries, resulting in significant pain, disability, and healthcare cost. As many as 2.5 million individuals sustain Achilles tendon ruptures each year and the incidence is rising. This trend is due, in part, to an increase in athletic participation across individuals of all ages.
Complete Achilles tendon ruptures occur most commonly at the mid-substance, but also distally at the insertion site or proximally at the myotendinous junction. These can be traumatic and devastating injuries, resulting in significant pain, disability, and healthcare cost. As many as 2.5 million individuals sustain Achilles tendon ruptures each year and the incidence is rising. This trend is due, in part, to an increase in athletic participation across individuals of all ages.


